Last updated on April 9th, 2022
Do you feel exhausted day after day? Do you get up during the night? It might show shallow breathing resulting from sleep apnea. If a person is diabetic, it is crucial to managing sleep apnea. As per the NIH, 18 million individuals experience sleep apnea. And up to 80 percent of individuals remain undiagnosed. If a person is diabetic, sleep apnea can increase the trouble while managing diabetes. When a person’s breathing pauses while sleeping, there is an increase in carbon dioxide in the blood. This causes:
- Long-term raised blood pressure
- Insulin resistance. The body fails to use insulin. This results in more sugar in the bloodstream causing high blood glucose levels.
- Early morning headaches
- A higher occurrence of cardiac problems

What is Sleep Apnea?
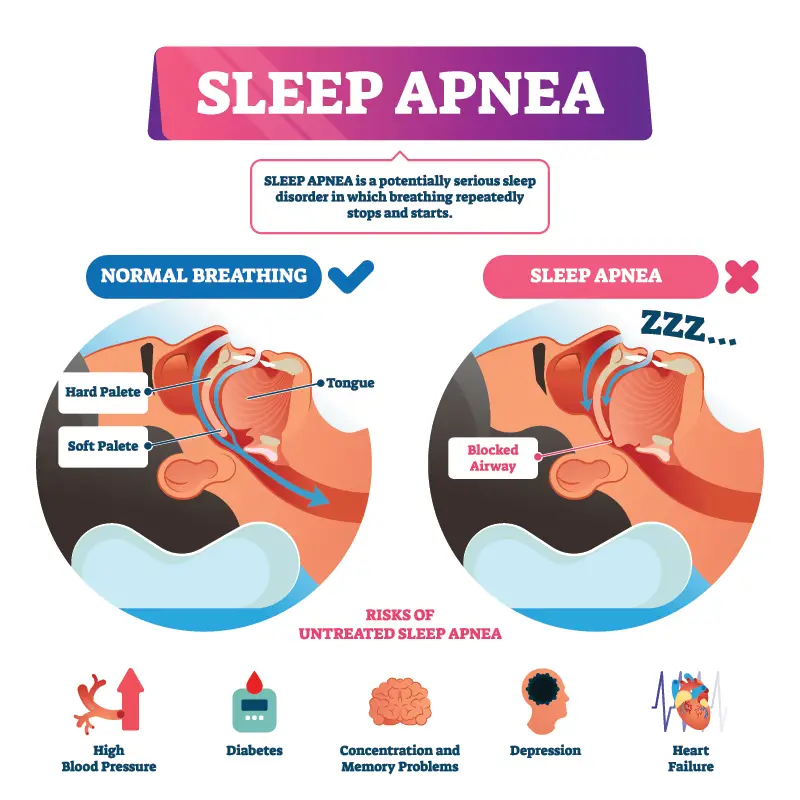
Sleep apnea is the condition of demonstrating breathing pauses while sleeping. The periods of stopped breathing are apneas. These occur due to an obstruction of the upper airway. Apnea indicates many brief arousal events during the night. A person remains unaware of such sleep disturbances. Sleep apnea gives rise to low oxygen levels in the blood. This is because the blockages prevent air from entering the lungs. Also, the low oxygen levels influence the brain and heart function. Up to 2/3rds of individuals with sleep apnea are expected to be heavier than the general population.
Sleep apnea modifies the sleep cycle and sleep phases. Few studies have associated modified sleep stages with a reduced growth hormone. It is responsible for body composition including body fat, muscle, and abdominal fat. A possible relationship between sleep apnea and the development of diabetes also exists.

The Connection Between Sleep Apnea and Diabetes
Unmanaged sleep apnea increases the sugar content. It may also cause poor quality of life due to chronic fatigue. Besides, it can trigger cardiovascular problems. Thus, it becomes so important to get their condition diagnosed and treated.
Sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes coincide. Coexistence is because of some shared risk factors like obesity. The more severe the sleep apnea in a type 2 diabetic is the poorer their levels of sugar control. Sleep apnea and its connection with type 2 diabetes have a lot to do with weight. Individuals with type 2 diabetes might be obese, insulin-resistant, and have huge visceral fat. The extra weight drops down the neck and throat tissues into the airway. And, this results in a blockage.
Also, sleep apnea may increase the blood sugar levels due to:
- stress linked with chronic sleep deprivation
- sudden awakenings in the night
During stress, the body releases stress hormones. These hormones release stored glucose into the liver. Gradually, the increase in blood glucose levels may also add to insulin resistance.
Causes of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea might be genetically associated. The condition is mostly found in:
- obese or overweight people
- people who smoke
- above 40 years of age
- Improper sleep or rest may also cause a lack of motivation to exercise or have meals. This arises irritability affecting relationships with family and friends. Also, sleepiness may cause individuals to forget to consume their medicines. This may also cause further diabetes complications.
Types of Sleep Apnea
There are various forms of sleep apnea. These can be obstructive sleep apnea (or OSA). OSA is the condition that interrupts breathing by a physical block to airflow. Snoring is a common problem in this. In type 2 diabetics, it is a common condition.
An increase in the seriousness of obstructive sleep apnea correlates with inferior glucose control. A diabetic person can have the following signs including:
- Depression
- Irritation
- Snoring
- Daytime sleepiness
- Sexual impairment
- Tiredness and fatigue
Also Read: Early Signs of Diabetes
How to Test for Sleep Apnea
The most common signs of obstructive sleep apnea are:
- loud, constant snoring (Remember that not all snorers have sleep apnea)
- pauses followed by gasping or choking
- Chronic fatigue
- Problems concentrating
- Mood swings
- Difficulty in blood pressure control
- Trouble in regulating the blood sugar levels
For a sleep apnea assessment, one must ask oneself the following STOP test questions. If the person answers yes to 2 or more of them, discuss with a doctor. These questions are:
- S – Do you snore noisily? (So loud that it can be heard via a closed door)
- T – Are you exhausted? (You fall asleep while driving or inactive during the day)
- O – Have you stopped breathing during sleep?
- P – Do you have a history of high blood pressure?
Also Read: Self Monitoring of Blood Glucose Levels
Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea
A doctor will ask the person about:
- sleep patterns
- whether there is difficulty in falling or staying asleep
- daytime sleepiness
- trouble in breathing while asleep (including snoring)
- any pain in the legs
- whether a person moves or kicks his or her legs during sleeping.
A doctor can perform a sleep study to learn whether a person has sleep apnea. For diagnosing sleep apnea, a person undergoes a sleep test. This test is a polysomnogram. It records body functions while a person is sleeping. Polysomnogram assesses:
- heart rate
- eye movements
- muscle activity
- electrical brain activity
- breathing and blood oxygen levels
Also Read: Best Glucometer in India
Sleep Apnea Treatment
Make lifestyle changes
A person with mild sleep apnea can treat it with simple lifestyle changes. These changes can be:
- weight loss. Helps open the throat by lessening the pressure on the neck.
- limiting alcohol and medications. They relax the tongue, cause it to fall back, and hinder the airway.
- quitting smoking
- relaxation and breathing techniques
- regular exercise, no later than some hours before bedtime
- avoiding caffeine or nicotine in the evening
- minimizing naps
- using the bed only for sleeping. Avoid lying on the bed to watch TV or read.
Too much sleepiness can be treated with medicine, Solriamfetol (Sunosi). This medicine is effective in keeping individuals with sleep apnea conscious for a long while.
Use a Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Machine
Treatment of sleep apnea is possible with CPAP. This is a mask that a person wears over nose and mouth while sleeping. Air pressure from the machine forces air via the nose. This prevents the closure of the nose during sleep.
Implantable Nerve Stimulator
Another option to manage sleep apnea is this stimulator. This was recently recommended for sleep apnea by the FDA.
Ask About Dental Devices
Dentists having expertise in treating sleep apnea help design custom devices. These can help in opening the airway during sleep.
Consider Surgery
Various procedures can reset the lower jaw or expand the breathing passages. They stiffen, shrink, or remove excess tissues present in the throat or mouth. These techniques physically expand the airway and decrease its collapse. Also, they obstruct the air passages while a person is sleeping.
If a person is type 2 diabetic, it’s important to check the signs of sleep apnea. Also, a proper diagnosis and its treatment is a must. It greatly improves blood glucose levels and sleep quality. Also, if a person is type 2 diabetic, it is simpler for the person to control. This is possible if he or she removes the stress hormones resulting from these frequent sleep troubles.
Also Read: A1c Chart
CPAP Therapy Relieves Sleep Apnea and May Control Diabetes
Since sleep apnea and diabetes seem to be associated. And, treating the sleep disorder may assist in diabetes improvement. However, studies assess the effect of using the gold standard for treating sleep apnea treatment. This gold standard is continuous positive airway pressure or CPAP therapy. It shows mixed results.
Studies state that CPAP therapy improves diabetes. A 2012 study looked at whether CPAP could help in diabetes control. They gave ½ participants the CPAP treatment, while other ½ sham CPAP for 8 weeks. The therapy didn’t bring blood sugar levels back to normal. However, it improved insulin sensitivity in individuals with severe sleep apnea.
Also Read: Home Remedies For Diabetes
Other Relationships Between Sleep and Diabetes
People having poor sleep habits are at a higher risk of obesity and developing type 2 diabetes. Chronic sleep problems cause insulin resistance. In turn, results in high blood sugar and diabetes. Sleep problems affect hormones regulating a person’s appetite. Findings associate insufficient sleep with reduced levels of the hormone leptin. This hormone regulates the metabolism of carbs. Low leptin levels increase the body’s craving for carbs irrespective of the calorie number consumed.
Summary
Sleep apnea is risky as it affects the oxygen concentration within the bloodstream. Also, it plays havoc with sleep patterns. Sleep apnea may also lead to daytime fatigue in more severe cases. If a person is diabetic, he or she must know he has sleep apnea. Because the person has to manage the sleep apnea for managing diabetes. A person feels much better with a good night’s rest!
Experts guide people with sleep apnea (either mild or severe) to undergo a diabetes test. Sleep apnea might vary from very mild to serious. It gets assessed by the number of apneas and hypopneas per night. Also, on the improvement of the sugar levels, apnea gets improved. And, now it’s possible to reverse the diabetic condition. The platform is completely cost-effective and user-friendly, Breathe Well-Being!! Book a consultation for your natural reversal. No strict diets for controlling diabetes. 10000+ success rates in reversals. 90% stoppage of medicines. Clinically proven program. Hurry up and grab the deals!!
FAQs:
Do diabetics snore?
If a person is diabetic and he or she snores, the two conditions might associate. Few snorers experience obstructive sleep apnea. Up to 90% of individuals with OSA are unmindful of their condition. While many people are diabetics.
What foods a person must avoid with sleep apnea?
Burgers, bacon, lamb, steak, pork, and sausage are meats with high saturated fats. Consuming an excess of such foods may inflame the body. And this can lead to cardiovascular problems. This is the biggest factor if a person experiences sleep apnea. Thus, it is good to avoid consuming these products.
How many hours of sleep are a must for a diabetic?
To keep the glucose level balanced, at least 7 hours of sleep every night is enough. For a person who works at night or has rotating shifts: maintain regular meal and sleep times on holidays.
Does sleep apnea influence blood pressure?
Sudden falls in blood oxygen levels enhance blood pressure and strain the heart. Obstructive sleep apnea enhances the risk of high blood pressure.
Does glucose worsen sleep apnea?
Consumption of loads of glucose might trigger an inflammatory response in the body. This response worsens sleep apnea. In addition, refined carbohydrates may add to weight gain. Obesity is one of the main risk factors for sleep apnea.
Why do diabetics face difficulty during sleeping?
It is estimated that 1 in 2 type 2 diabetic patients face sleep problems. And this is due to the unstable blood glucose levels and associated diabetes signs. Also, hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia during the night may cause insomnia and next-day fatigue.
References:
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/sleep-apnea-can-make-managing-diabetes-more-difficult-what-you-need-to-know/
- https://www.everydayhealth.com/type-2-diabetes/living-with/sleep-apnea-connection/
Last Updated on by Dr. Damanjit Duggal
Disclaimer
This site provides educational content; however, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Readers should consult their healthcare professional for personalised guidance. We work hard to provide accurate and helpful information. Your well-being is important to us, and we value your feedback. To learn more, visit our editorial policy page for details on our content guidelines and the content creation process.

 English
English